|
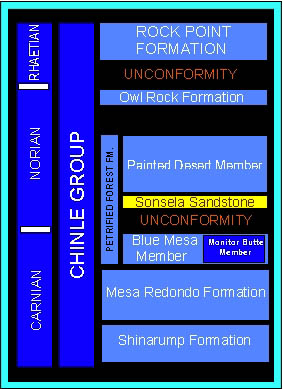
General Overview The late Triassic Chinle Group represents lacustrine and fluvial terrestrial deposits some 225 million years in age. Sediments contained primarily in North Eastern Arizona include sandstones, mudstones, claystones and shale. Beds of conglomerates and gypsums complete the formation which extends up into the Four Corners Area. The Chinle is famous for its collection of unique fossil fauna and flora, which incudes the earliest dinosaurs, metopasaurs, phytosaurs and mammal like reptiles. We also find the remains of freshwater lungfish, sharks and horseshoe crabs, and a rich floral assemblage of cycads, tree ferns, giant neocalamites herbs, and of course, Araucarioxylon, the giant petrified conifers which made famous the Petrified Forest near Holbrook. The Chinle Group consists of in ascending order, the Shinarump, Mesa Redondo, Monitor Butte, and Petrified Forest formation which includes the Blue Mesa Member, Sonsela Sandstone, and Painted Desert Members, then the Petrified Forest Formation is overlain by the Owl Rock and Rock Point Formations. In the southernmost extensions of the Chinle it is underlain by the Triassic Moenkopi Formation which is primarily a series of redbeds, but on the northern boundary of the state, is underlain by the Permian Kaibab formation. We found a great many beds in the Chinle with reworked Kaibab cherts containing Paleozoic fossils.
|